How New GCodes Are Authored
I wanted to provide an example of how new GCodes are added to firmwares in off-the-shelf workflows, since it is somewhat common that machine developers need to work across these layers when developing new equipment.
- GCode Programs like the one below use
GxxandMxxcodes to define program operations.
L01 G21 ; use millimeters
L02 G28 ; run the homing routine
L03 G92 X110 Y120 Z30 ; set current position to (110, 120, 30)
L04
L05 G0 X10 Y10 Z10 F6000 ; "rapid" in *units per minute*
L06
L07 M3 S5000 ; turn the spindle on, at 5000 RPM
L08
L09 G1 Z-3.5 F100 ; plunge from (10, 10, 10) to (10, 10, -3.5)
L10 G1 X20 ; draw a square, go to the right,
L11 G1 Y20 ; go backwards 10mm
L12 G1 X10 ; go to the left 10mm
L13 G1 Y10 ; go forwards 10mm
L14 G1 Z10 ; go up to Z10, exiting the material
L15
L16 M5 ; stop the spindle
L17 G0 X110 Y120 Z30 ; return to the position after homing (at 6000)
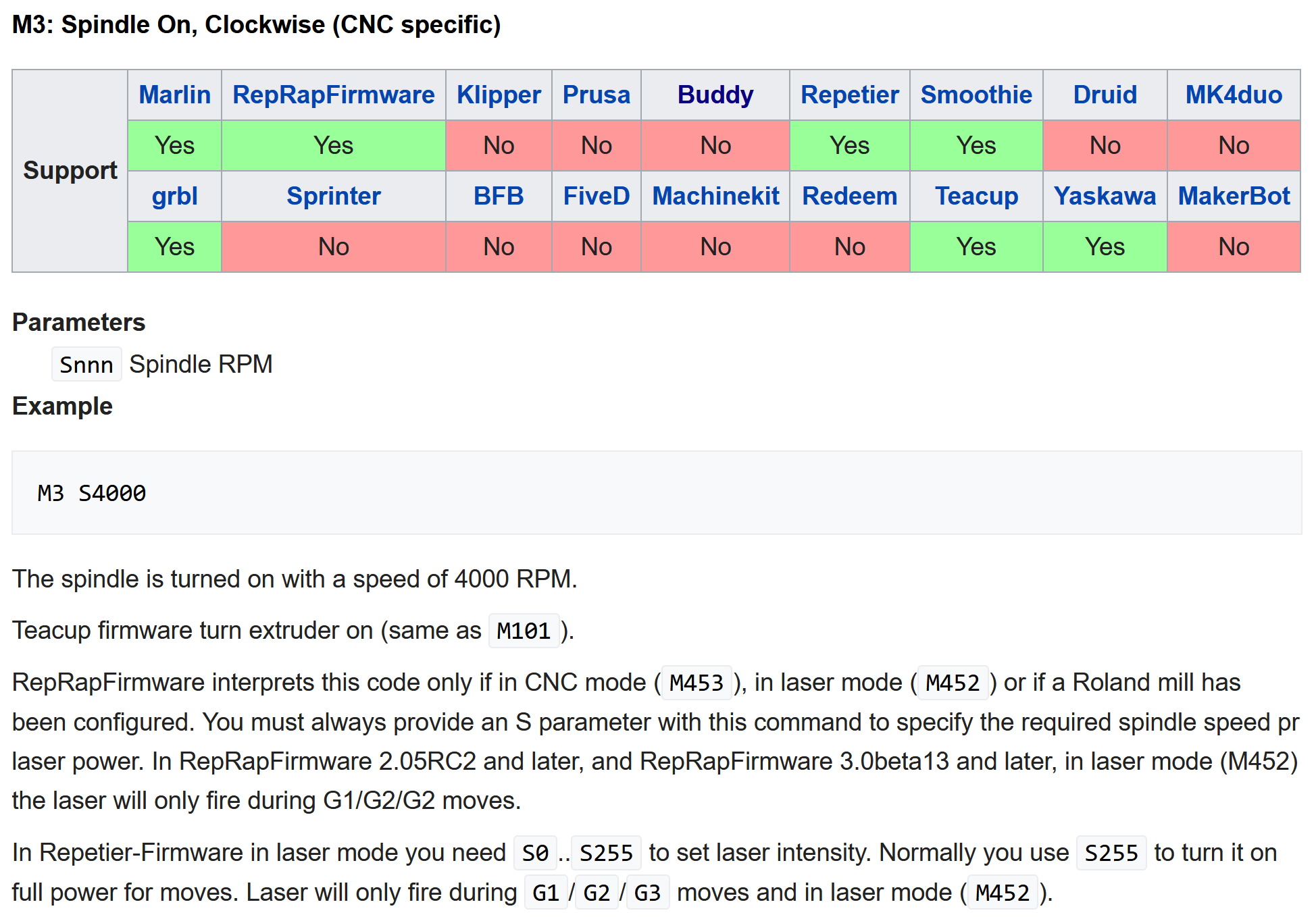
- Machine programmers use resources like RepRap’s GCode Table to track what individual codes (like the
M3at Line 07 above) should do (and whether they are supported on the particular firmware they are using). Machine vendors with closed controllers should provide a similar table.
- Each of those codes is implemented in firmware, below I show the snippet of cpp that defines the switch for any “M” code - here I am looking at the Marlin firmware, popular among hobbyist FFF printers. This snippet shows some compile flags
HAS_CUTTERthat are related to build-time firmware configurations. So, even if we can find this snippet of code, we still won’t know if the firmware that is currently running on our controller has implemented it - we would need to look at the configuration file as well.
// in Marlin/src/GCode/GCode.cpp
// line 477
case 'M': switch (parser.codenum) {
// ...
#if HAS_CUTTER
case 3: M3_M4(false); break; // M3: Turn ON Laser | Spindle (clockwise), set Power | Speed
case 4: M3_M4(true ); break; // M4: Turn ON Laser | Spindle (counter-clockwise), set Power | Speed
case 5: M5(); break; // M5: Turn OFF Laser | Spindle
#endif
// ...
}
// exit line 1172
- The actual implementation of the code can be found deeper in the firmware source, with another selection of compiler flags (
ENABLED(LASER_FEATURE)).
// in Marlin/src/GCode/control/M3-M5.cpp
void GCodeSuite::M3_M4(const bool is_M4) {
#if LASER_SAFETY_TIMEOUT_MS > 0
reset_stepper_timeout(); // Reset timeout to allow subsequent G-code to power the laser (imm.)
#endif
if (cutter.cutter_mode == CUTTER_MODE_STANDARD)
planner.synchronize(); // Wait for previous movement commands (G0/G1/G2/G3) to complete before changing power
#if ENABLED(LASER_FEATURE)
if (parser.seen_test('I')) {
cutter.cutter_mode = is_M4 ? CUTTER_MODE_DYNAMIC : CUTTER_MODE_CONTINUOUS;
cutter.inline_power(0);
cutter.set_enabled(true);
}
#endif
auto get_s_power = [] {
if (parser.seenval('S')) {
const float v = parser.value_float();
cutter.menuPower = cutter.unitPower = TERN(LASER_POWER_TRAP, constrain( v, 0, CUTTER_POWER_MAX), cutter.power_to_range(v));
}
else if (parser.seenval('O')) { // pwr in PWM units
const float v = parser.value_float();
cutter.menuPower = cutter.unitPower = CUTTER_PWM_TO_SPWR(constrain(v, 0, 255));
}
else if (cutter.cutter_mode == CUTTER_MODE_STANDARD)
cutter.menuPower = cutter.unitPower = cutter.cpwr_to_upwr(SPEED_POWER_STARTUP);
// PWM not implied, power converted to OCR from unit definition and on/off if not PWM.
cutter.power = TERN(SPINDLE_LASER_USE_PWM, cutter.upower_to_ocr(cutter.unitPower), cutter.unitPower > 0 ? 255 : 0);
};
if (cutter.cutter_mode == CUTTER_MODE_CONTINUOUS || cutter.cutter_mode == CUTTER_MODE_DYNAMIC) { // Laser power in inline mode
#if ENABLED(LASER_FEATURE)
planner.laser_inline.status.isPowered = true; // M3 or M4 is powered either way
get_s_power(); // Update cutter.power if seen
#if ENABLED(LASER_POWER_SYNC)
// With power sync we only set power so it does not effect queued inline power sets
planner.buffer_sync_block(BLOCK_BIT_LASER_PWR); // Send the flag, queueing inline power
#else
planner.synchronize();
cutter.inline_power(cutter.power);
#endif
#endif
}
else {
cutter.set_enabled(true);
get_s_power();
cutter.apply_power(
#if ENABLED(SPINDLE_SERVO)
cutter.unitPower
#elif ENABLED(SPINDLE_LASER_USE_PWM)
cutter.upower_to_ocr(cutter.unitPower)
#else
cutter.unitPower > 0 ? 255 : 0
#endif
);
TERN_(SPINDLE_CHANGE_DIR, cutter.set_reverse(is_M4));
}
}